If you are studying organic chemistry, chances are you searched for SN1 vs SN2 to clear confusion.
These two reactions look similar, but they work very differently.
Many students mix them up because both involve nucleophilic substitution and both replace one group with another.
The real confusion starts when questions ask which reaction will occur or why a reaction follows SN1 instead of SN2.
Exams, quizzes, and lab work often depend on this single choice. A small misunderstanding can cost big marks.
This guide solves that problem. You will get a quick answer, simple explanations, clear examples, and practical tips.
By the end, you will know how to identify SN1 and SN2 reactions in seconds, understand why they happen, and use the correct mechanism with confidence.
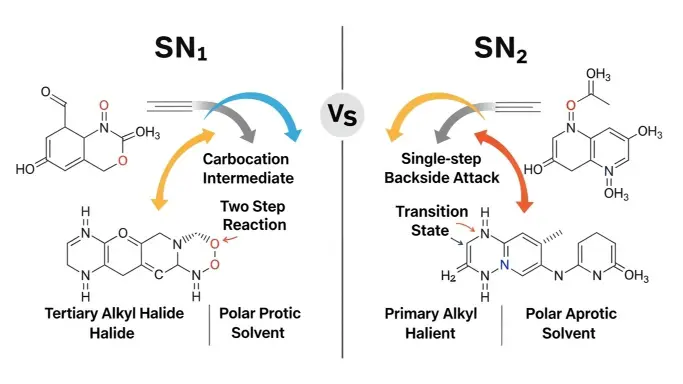
SN1 vs SN2 Quick Answer
SN1 is a two-step reaction that forms a carbocation first.
SN2 is a one-step reaction where everything happens at once.
Simple example:
- SN1: Tertiary alkyl halides in polar protic solvents
- SN2: Primary alkyl halides with strong nucleophiles
Memory tip:
- SN1 = Stepwise
- SN2 = Single step
The Origin of SN1 vs SN2
The terms SN1 and SN2 come from chemical kinetics:
- SN means Substitution Nucleophilic
- 1 means first-order reaction
- 2 means second-order reaction
These names were introduced to describe how reaction speed depends on concentration.
There are no spelling variations because these are scientific terms. The names are universal and used the same way worldwide.
British English vs American English Spelling
Unlike common word comparisons, SN1 vs SN2 has no spelling difference in British or American English.
| Aspect | British English | American English |
| Term | SN1, SN2 | SN1, SN2 |
| Meaning | Same | Same |
| Usage | Same | Same |
Key point: Scientific terms stay the same across all regions.
Which Should You Use: SN1 or SN2?
Choose based on structure and conditions, not location.
- Use SN1 when:
- Substrate is tertiary
- Weak nucleophile
- Polar protic solvent
- Substrate is tertiary
- Use SN2 when:
- Substrate is primary
- Strong nucleophile
- Polar aprotic solvent
- Substrate is primary
Common Mistakes with SN1 vs SN2
Many learners make these errors:
❌ Thinking SN1 happens in one step
✅ SN1 happens in two steps
❌ Using SN2 with tertiary substrates
✅ SN2 works best with primary substrates
❌ Forgetting solvent effects
✅ Solvent choice matters a lot
SN1 vs SN2 in Everyday Examples
- Exams: Identify reaction type from substrate
- Lab reports: Explain mechanism clearly
- Chemistry blogs: Compare reaction pathways
- Textbooks: Use diagrams for step clarity
Formal writing example:
“Due to carbocation stability, the reaction proceeds via an SN1 mechanism.”
SN1 vs SN2 Google Trends & Usage Data
Search interest for SN1 vs SN2 is highest in:
- United States
- India
- Pakistan
- United Kingdom
Most searches come from:
- Students
- Exam preparation
- Online chemistry courses
The keyword is popular during exam seasons and academic semesters.
SN1 vs SN2 Side-by-Side Comparison Table
| Feature | SN1 | SN2 |
| Steps | Two | One |
| Rate Law | First-order | Second-order |
| Carbocation | Yes | No |
| Best Substrate | Tertiary | Primary |
| Nucleophile | Weak | Strong |
FAQs About SN1 vs SN2
1. What does SN stand for?
Substitution Nucleophilic.
2. Which is faster, SN1 or SN2?
It depends on conditions, not speed alone.
3. Does SN1 cause rearrangements?
Yes, carbocation rearrangements are common.
4. Can secondary substrates do both?
Yes, depending on solvent and nucleophile.
5. Is SN2 stereospecific?
Yes, it causes inversion of configuration.
6. Do solvents affect SN1 and SN2?
Yes, very strongly.
7. Are SN1 and SN2 used in real life?
Yes, in drug and chemical synthesis.
Conclusion
Understanding SN1 vs SN2 is essential for mastering organic chemistry.
The key is not memorization but recognition. Look at the substrate, nucleophile, and solvent.
SN1 reactions happen step by step and form carbocations, while SN2 reactions occur in a single, clean step.
There are no spelling or regional differences in these terms, making them universal across textbooks and classrooms worldwide.
Once you learn the patterns, choosing the correct mechanism becomes easy and fast.
If you are preparing for exams or improving your chemistry basics, mastering SN1 vs SN2 will boost both confidence and accuracy.

I am Victor Stone, a passionate learner and content creator at Grammexa.com, where language meets clarity.
I am dedicated to simplifying confusing words, grammar rules, and “vs” comparisons for modern readers.
I am here to make English easy, accurate, and trending one explanation at a time.